The AI-SPRINT European Project uses the OSCAR serverless platform to support the scalable execution of the inference phase of AI models along the computing continuum in all the uses cases: personalized healthcare, maintenance & inspection and, finally, farming 4.0.
This post briefly summarises the integration.
What is AI-SPRINT?
The AI-SPRINT project aims to:
- Create new tools for developing AI applications whose components will run seamlessly and securely across distributed heterogeneous infrastructures.
- Provide advanced strategies to design and optimally partition AI models considering model accuracy, application performance, security and privacy constraints.
- Deliver solutions for the agile delivery and secure automatic deployment and execution of AI applications and models across the cloud-edge continuum while preserving the privacy of users’ data.
- Implement a runtime environment to monitor application executions with data load variations of sensor streams or component failures.
- Support continuous training and application architecture enhancement to add new data to AI applications, exploiting novel edge AI-based sensor capabilities.
There are three use cases tackled by AI-SPRINT as shown in the figure below.

We provide a brief description of the use case, focusing on the integration of the OSCAR plaform. Further details are available in the AI-SPRINT website.
Personalized Healthcare
The Personalized Healthcare use case is led by the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC) and it aims at deploying AI models for health monitoring using wearable and mobile devices. Specifically, it focuses on assessing stroke risk by combining quantitative data (sensor data) and qualitative data (lifestyle information) to create risk stratification models operating in the edge-cloud continuum.
Continuous and non-invasive AI-driven monitoring through smart wearable and mobile devices is an excellent strategy for preventing stroke. The synergy of the workload between IoT, cloud and edge allows the capture of data and prevents strokes in real-time and in future, improves AI models. The most critical issue in this project is ensuring the protection of sensitive data through GDPR compliance and mechanisms to preserve privacy and security, including data anonymization and federated learning.
As shown in the figure below, OSCAR is used to execute in a scalable manner the inference requests of the pre-trained AI models that have been developed to assess risk stroke, whenever new data is available. An OSCAR cluster was deployed at Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) to perform the executions. The cluster was integrated with SCONE to support confidential computing while performing in-memory computing. It was also integrated with PyCOMPS a Python binding for the COMPSs system, which provides a task-based programming model to ease the development of applications for distributed infrastructures. The OSCAR jobs running in the Kubernetes cluster transparently exploited the inner parallelism of the multiple virtual CPUs of the underlying containers via PyCOMPSs (further information on how to use OSCAR with COMPSs is available in this post).
The OSCAR cluster was used in a BSC hackathon for contributing to La Marató de TV3, a public Catalan charity effort.
Further information about this use case is available in the Personalized Healthcare section in the AI-SPRINT web site.
Maintenance & Inspection
Maintenance & Inspection use case, led by TTA, exploits AI models for identifying windmill blade damage based on vision and thermal images collected by drones. The relevant images are selected at the edge (ground station) and only relevant data are transmitted over the edge-cloud channel. Edge processing will also be in charge of calling for a new acquisition (detailed images of specific regions) when required. AI-SPRINT assets will enable optimal interaction of cloud-based (computationally intensive, longer) analysis and local processing using lighter data pattern recognition routines.
Previously, all the computation was made as a batch job. Every step processes all the data then we proceed to the next one only when a previous step is finished:
- Data acquisition
- Data upload
- Initial data analysis
- Final data analysis and report preparation
The integration of OSCAR in this use case is shown in the figure below. Images are acquired by the Drone and processed in several OSCAR clusters, which can be deployed in several layers of the compute continuum. In particular, OSCAR can be deployed in low-powered devices such as NVIDIA Jetson devices or clusters of Raspberry PIs.
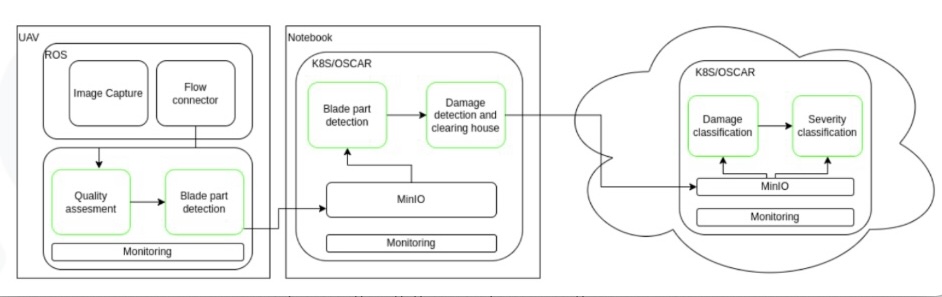
OSCAR was deemed a crucial component to provide serverless-style processing of images with seamless monitoring an scaling. It was used for edge and cloud processing (object detection and damage classification and assessment).
Further information about this use case is available in the Maintenance and Inspection section in the AI-SPRINT web site.
Farming 4.0
The primary task of the Farming 4.0 use case, led by Skaylink is to develop an AI-driven system to compute the required quantity of phytosanitary treatment. It uses edge and intelligent sensors to optimise phytosanitary treatments, helping to preserve and protect the environment with the support of AI-SPRINT technology
The tractor is in motion during computation time. Aboard the tractor are sensors that provide inputs to estimate the phytosanitary treatment volume. So, the computation must be in real-time, around 2-3 seconds of time frame.
To achieve this goal. The computation is made in an OSCAR cluster on edge devices. First, the camera system is started, and a continuous stream of depth information is recorded and saved as images with a frequency of 2-4 frames per second. Saving each image triggers a synchronous call of the volume estimation function that runs in an OSCAR cluster. After the internal calculations, the volume information for each sprayer is sent as output, as well as at which the sprayer should switch to the new setting.
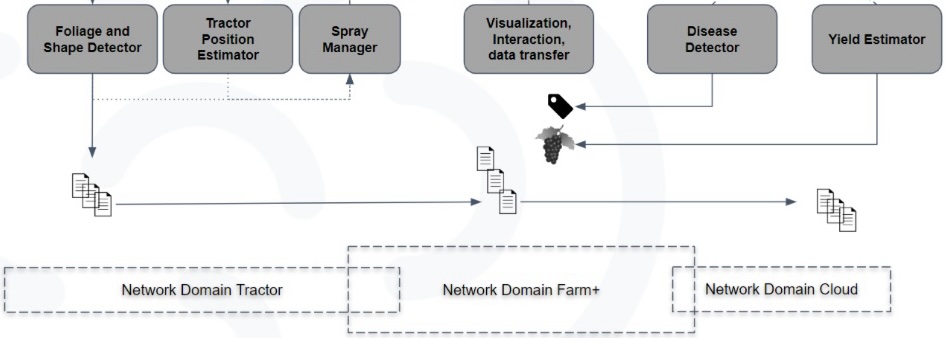
In parallel, the application infrastructure runs on the edge device with the possibility of cloud deployment. For this, the necessary steps for the workflow were split up into components designed to run as FaaS to allow for re-deployment between edge and cloud as needed. The Infrastructure Manager (IM) was used to deploy an OSCAR cluster in Amazon Web Services (AWS). The synergy between OSCAR and IM solves the interoperability problem between clouds and edge-cloud when you work for the complete stack with a specific cloud provider.
OSCAR was integrated with edge devices, such as Smart Farming Devices (SFD) which is in the tractor, to enable real-time decision-making and treatment adjustments based on volume estimation. This integration allows for the execution of inferences critical for adaptive treatment. Additionally, OSCAR facilitates the deployment of components for yield estimation and disease detection, enhancing overall productivity.
Further information about this use case is available in the Farming section in the AI-SPRINT web site.
OSCAR and IM are developed by the GRyCAP research group at the Universitat Politècnica de València.
