Blog
Guide to create a service in OSCAR
This is a step by step guide to show developers how to create their first service in OSCAR.
Previous steps:
Deploy the OSCAR cluster
Follow the deployment instructions with the IM Dashboard. Alternatively, you can execute this script to deploy the cluster locally using kind. Kind will name the cluster oscar-test.
curl -sSL http://go.oscar.grycap.net | bash
Log in to the OSCAR UI using the previously provided credentials to verify that the cluster has been successfully deployed, and save them to use later in the guide.
Read more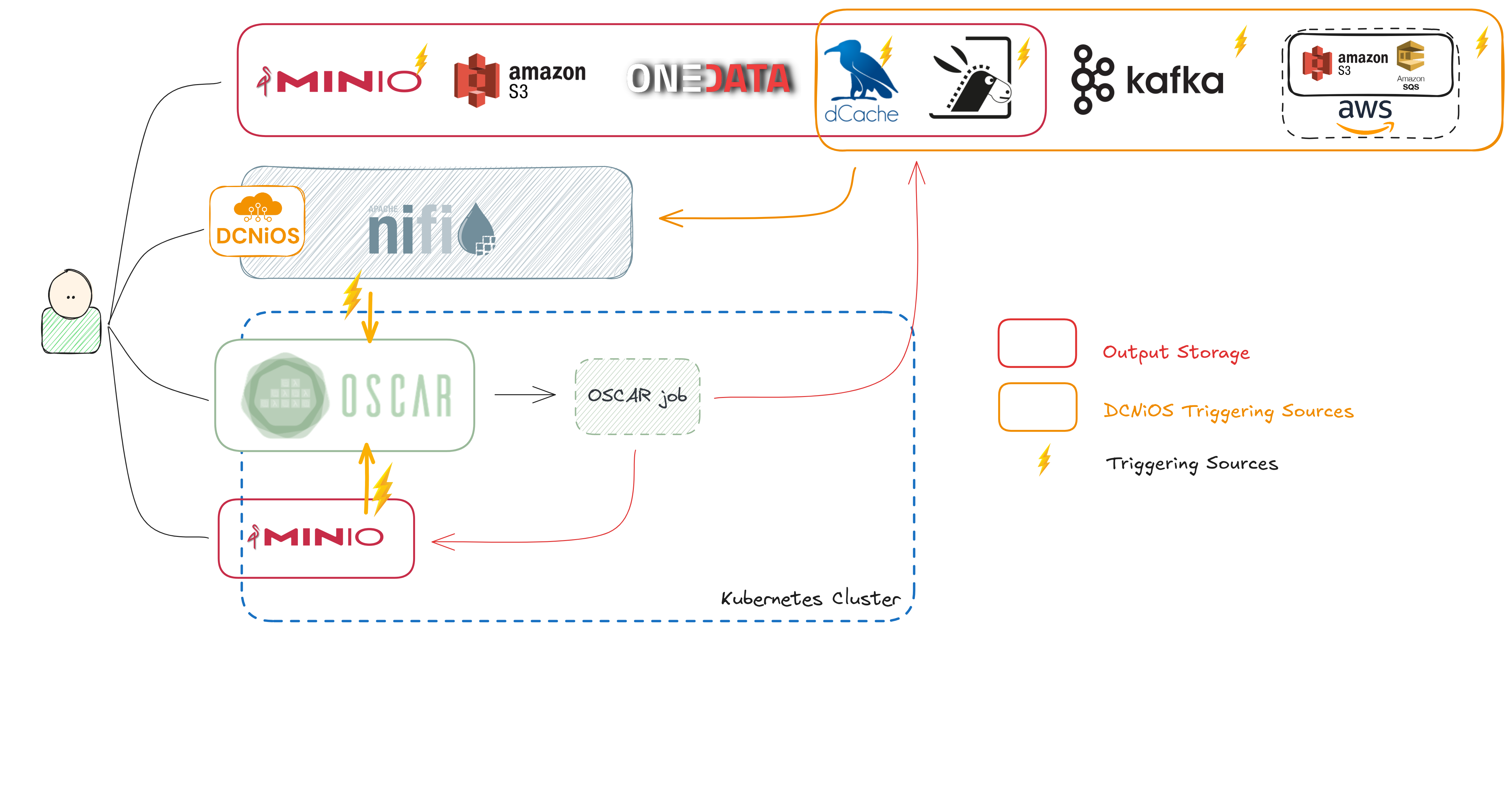
Digital Twin science made serverless: evolving OSCAR within interTwin
This post summarizes the work carried out in the InterTwin project to extend the OSCAR serverless platform across the cloud–HPC continuum. We developed DCNiOS, a Data Connector through Apache NiFi for OSCAR, that facilitates the creation of event-driven dataflows connecting storages system like dCache, S3 (via SQS), Kafka, and Rucio, enabled seamless offloading of OSCAR workloads to HPC via interLink, added interactive Jupyter notebooks as exposed services, and integrated Common Workflow Language (CWL) using oscar-python from them.

Bringing Serverless to Marine Science: Our Journey with OSCAR and iMagine.
The iMagine European Project uses the OSCAR serverless platform to support the scalable execution of the inference phase of marine AI models in mature thematic services. As the project has finished recently (in August 2025), in this post, we want to highlight the achievements and
What is iMagine?
The iMagine project is an EU-funded project with the mission to deploy, operate, validate, and promote a dedicated iMagine AI framework and platform connected to EOSC, giving researchers in aquatic sciences open access to a diverse portfolio of AI based image analysis services and image repositories from multiple RIs, working on and of relevance to the overarching theme of Healthy oceans, seas, coastal and inland waters. This AI framework is based on the AI4OS software stack provided by the AI4EOSC project (read our post for more details about AI4EOSC and the role of OSCAR in the project).
Read more
Serverless Computing for Artificial Intelligence: The OSCAR–AI4EOSC Integration Story.
The AI4EOSC European Project uses the OSCAR serverless platform to support the scalable execution of the inference phase of AI models. As the project has come to its end in August 2025, in this post, we want to briefly summarize the achievements and integrations performed during it.
What is AI4EOSC?
AI4EOSC stands for “Artificial Intelligence for the European Open Science Cloud.” It is an initiative aimed at integrating artificial intelligence (AI) technologies into the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC), a federated ecosystem that enables researchers to access, process, and share data and services across Europe.
Read more
Composing AI Inference pipelines with Node-RED & Flowfuse
In this post, we are going to learn about composing AI inference workflows by invoking OSCAR services with Node-RED & FlowFuse. Both tools facilitate the graphical composition of pipelines, a user-friendly approach with drag & drop capabilities that allow us to easily compose a pipeline involving different OSCAR services. For that, we have prepared a video demo that we invite you to watch. These developments are part of AI4-Compose, a component of the AI4OS stack, created in the AI4EOSC project.
Read moreComposing AI Inference workflows based on OSCAR services with Elyra in EGI Notebooks
In this post, we will learn about composing AI inference workflows by invoking OSCAR services with Elyra. This tool is an extension for Jupyter Notebooks and facilitates the graphical composition of pipelines, which allows us to easily compose a pipeline involving different OSCAR services. For that, we have recovered the next video demo that we invite you to watch. These developments are part of AI4-Compose, a component of the AI4OS stack, created in the AI4EOSC project.
Read more
Integration of OSCAR in AI-SPRINT Use Cases
The AI-SPRINT European Project uses the OSCAR serverless platform to support the scalable execution of the inference phase of AI models along the computing continuum in all the uses cases: personalized healthcare, maintenance & inspection and, finally, farming 4.0.
This post briefly summarises the integration.
What is AI-SPRINT?
The AI-SPRINT project aims to:
- Create new tools for developing AI applications whose components will run seamlessly and securely across distributed heterogeneous infrastructures.
- Provide advanced strategies to design and optimally partition AI models considering model accuracy, application performance, security and privacy constraints.
- Deliver solutions for the agile delivery and secure automatic deployment and execution of AI applications and models across the cloud-edge continuum while preserving the privacy of users’ data.
- Implement a runtime environment to monitor application executions with data load variations of sensor streams or component failures.
- Support continuous training and application architecture enhancement to add new data to AI applications, exploiting novel edge AI-based sensor capabilities.
There are three use cases tackled by AI-SPRINT as shown in the figure below.
Read more
Data-driven Processing with dCache, Apache Nifi and OSCAR
This post describes the integration between OSCAR and dCache. Data stored in dCache triggers the invocation of an OSCAR service to perform the processing of that data file within the scalable OSCAR cluster. This work is being done in the context of the InterTwin EU project.

What is dCache?
dCache is a system for storing data in distributed and heterogenous server nodes that works like a single virtual filesystem tree. The system can be expanded or contracted by adding/removing data servers at any time. dCache is developed by DESY.
Read more
Design of workflows across OSCAR services with Node-RED (Part 2).
In this post, the work with Node-RED and its interaction with OSCAR services will be continued. Two workflows will be presented where you interact with OSCAR services using the Dashboard tool, which will ultimately provide a web interface for the user. In general, there will be a choreography of various OSCAR services, where the backend part will be in the workflow programming part and the frontend will be in the web interface provided by the dashboard.
Read more
Design of workflows across OSCAR services with Node-RED (Part 1).
In this post, we will be explaining the integration of Node-RED software with OSCAR. The necessary tools will be given to achieve workflows between OSCAR and Node-RED simply and intuitively through flow-based programming techniques. For this, a series of nodes and subflows have been developed, which will interact with a set of services, previously deployed in an OSCAR cluster.
1. Introduction to working with Node-RED software.
Node-RED is a tool to communicate services in a very convenient way. It greatly simplifies the task of programming on the server side thanks to visual programming.
Read more
Use COMPSs with OSCAR
This is a tutorial to integrate COMPSs with OSCAR. In this post, we will explain what COMPSs is and the integration with OSCAR to support parallel processing within an on-premises serverless platform.
What is OSCAR?
OSCAR is an open-source serverless platform for event-driven data-processing containerized applications that execute on elastic Kubernetes clusters that are dynamically provisioned on multiple Clouds.
What is COMPSs?
COMP Superscalar (COMPSs) is a task-based programming model which aims to ease the development of applications for distributed infrastructures, such as large High-Performance clusters (HPC), clouds and container managed clusters. COMPSs provides a programming interface for the development of the applications and a runtime system that exploits the inherent parallelism of applications at execution time.
Read more
Invoking an OSCAR Service from an EGI Jupyter Notebook
In this post, we are going to showcase the usage of the OSCAR Python API, implemented to interact with OSCAR clusters and its services through EGI Notebooks, a tool based on Jupyter for data analysis.
Through this post, we will create an EGI Notebook and test the OSCAR API with a simple service (cowsay service) that receives a text input and shows it on the terminal.
You can see more information about the use of EGI notebooks on https://docs.egi.eu/users/dev-env/notebooks/
Read more
Why use OSCAR as a serverless AI/ML model inference platform?
What is OSCAR?
OSCAR is an open-source serverless platform for event-driven data-processing containerized applications that execute on elastic Kubernetes clusters that are dynamically provisioned on multiple Clouds.
OSCAR can be used as an effective serverless platform for scalable AI/ML model inference to achieve the following benefits:
- Ability to run AI model inference on disparate computing platform architectures, multiple Cloud providers and across the edge-to-cloud continuum, including your computer for easier testing.
- Seamless scalability for AI model inference regardless of the number of requests from your users, provided that the underlying computing platform provides enough hardware resources.
Here are the main reasons why.
Read more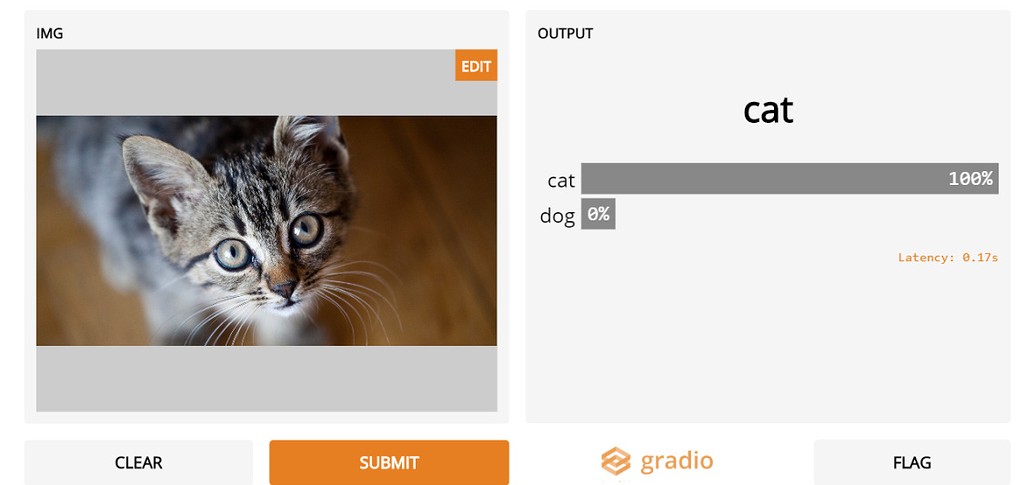
User interfaces with Gradio for AI model inference in OSCAR services
What is Gradio?
Gradio is a Python library for building user web interfaces for Machine Learning (ML) applications. Those interfaces can be customized with the components that Gradio provides, like Textbox, File, Video, Audio, Image, and Dataframe in a short period, saving time. Also, an authentication process can be implemented to grant access to the user for model inference. This allows to create nice web-based user interfaces for the inference process of a ML application.
Read more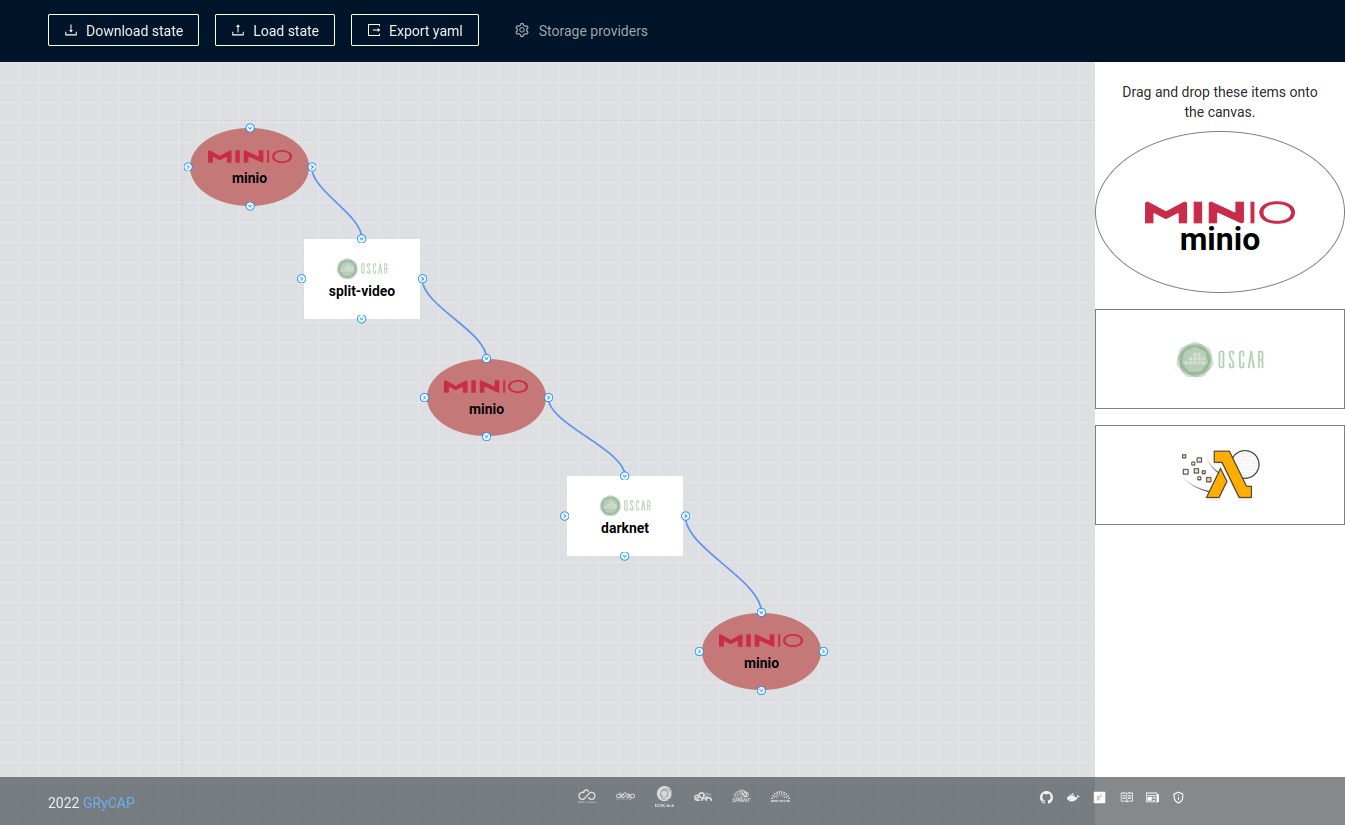
FDL Composer to create a workflow with OSCAR
FDL-Composer is a tool to visually design workflows for OSCAR and SCAR. We are going to simulate the example video-process
This example supports highly-scalable event-driven video analysis using ffmpeg to extract keyframes of the video and Darknet to perform object recognition on the keyframes. It requires two OSCAR services: one where the video is going to get split into frames, and another to process those frames. It also requires three MinIO buckets. One for the input. One for the output. And the last one for the connection between both services. So when a video is uploaded to the input bucket, the “split video” OSCAR service will be triggered and let the frames in an intermediate bucket. That will trigger the “processing frame” OSCAR service. Furthermore, the result will be stored in the last bucket.
Read more
Using OSCAR as a FaaS platform for synchronous inference of a machine learning model
This guide aims to show the usage of the OSCAR platform for Machine Learning inference using a pre-trained Convolutional Neural network classification model by DEEP-Hybrid-DataCloud: the Plants species classifier, to classify plant pictures by specie. The PREDICT method works with an RGB image as input and returns a JSON with the top 5 predictions of the plant’s specie.
The example is going to be focused on synchronous invocations. OSCAR supports two types of invocations:
Read more
Guide to create a service in OSCAR
This is a step by step guide to show developers how to create their first service in OSCAR.
Previous steps:
Deploy the OSCAR cluster
Follow the deployment instructions with the IM Dashboard. Alternatively, you can execute this script to deploy the cluster locally using kind. Kind will name the cluster oscar-test.
curl -sSL http://go.oscar.grycap.net | bash
Log in to the OSCAR UI using the previously provided credentials to verify that the cluster has been successfully deployed, and save them to use later in the guide.
Read more
Convert Text to Speech with OSCAR
This use case implements text-to-speech transformation using the OSCAR serverless platform, where an input of plain text returns an audio file. There are two examples of implementing this use case:
- Google Speech library
- Pretrained model of Coqui
Previous step: Deploy the OSCAR cluster on an IaaS Cloud and install OSCAR-CLI
Follow the deployment instructions with the IM Dashboard. Alternatively, the folowing script can be executed locally.
curl -sSL http://go.oscar.grycap.net | bash
To create the service, we will use the command-line interface OSCAR-CLI.
Read more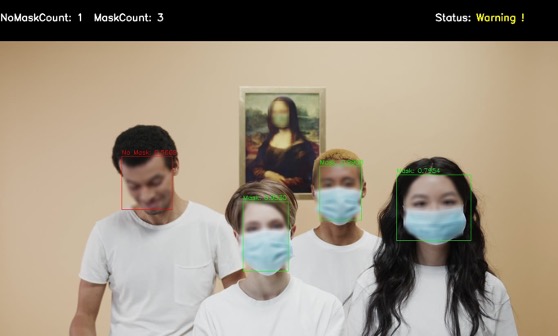
A Serverless Cloud-to-Edge Computing Continuum Approach for Edge AI inference
OSCAR is an open-source framework for data-processing serverless computing. Users upload files to an object storage which invokes a function responsible for processing each file. This runs on an elastic Kubernetes cluster, managed by the CLUES elasticity manager, that can be deployed on multiple Cloud providers thanks to the Infrastructure Manager (IM).
Functions can be chained to create data-driven serverless workflows which can run on different OSCAR clusters along several Cloud infrastructures. This way, the file-based output of a function is fed as input to another function through the corresponding object storage systems, thus using resources from multiple infrastructures.
Read more
Using OSCAR as a FaaS platform for scalable asynchronous inference of a machine learning model
OSCAR is a framework to efficiently support on-premises FaaS (Functions as a Service) for general-purpose file-processing computing applications. Users upload files to a bucket and this automatically triggers the execution of parallel invocations to a function responsible for processing each file. For example, you can deploy a machine learning inference environment by defining a function in your OSCAR cluster, and every time you upload an image to your bucket the inference process is triggered, and the result is stored.
Read more
Deployment of an OSCAR cluster in the EGI Federated Cloud
Here we present a step by step guide to help you deploy an OSCAR cluster in the EGI Federated Cloud, specifically in the EOSC-Synergy VO. We are using the IM Dashboard, a tool developed by the GRyCAP research group at the Universitat Politècnica de València to facilitate the deployment of infrastructures in a lot of cloud providers. Alternatively, you can follow our YouTube video, at the end of the post.
Step 1: Go the the IM Dashboard and click the button “Login with EGI-Check-in”.
Read more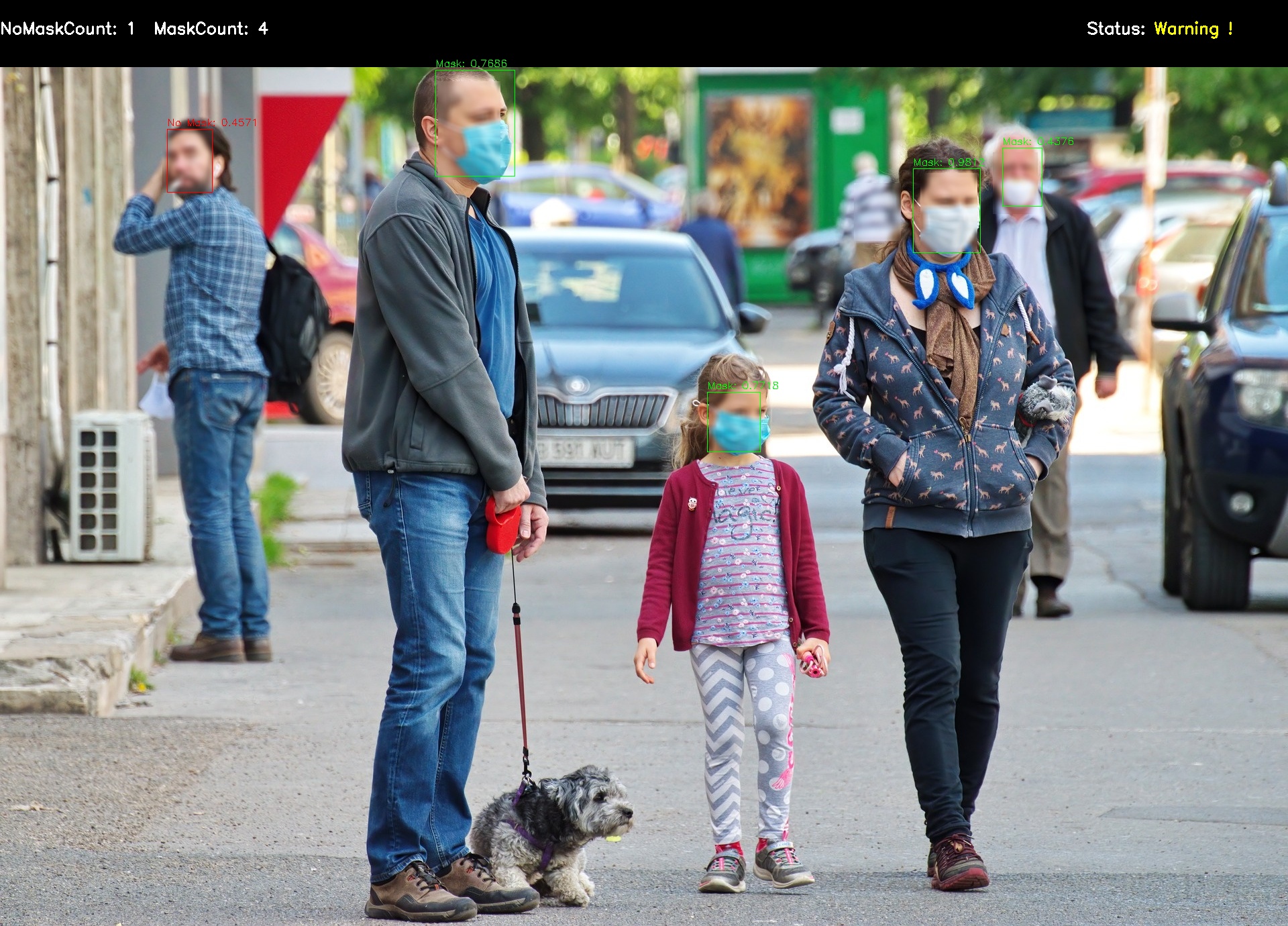
Event-driven inference of AI models for mask detection with the OSCAR serverless platform
What is OSCAR?
OSCAR is an open-source platform to support the Functions as a Service (FaaS) computing model for file-processing applications. It can be automatically deployed on multi-Clouds in order to create highly-parallel event-driven file-processing serverless applications that execute on customized runtime environments provided by Docker containers than run on an elastic Kubernetes cluster.
Why use OSCAR for inference of AI models?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) models are used once they have been trained in order to perform the inference phase on a set of files. This requires event-driven capabilities and automated provisioning of resources in order to cope with the dynamic changes in the workload. By using auto-scaled Kubernetes clusters, OSCAR can execute the inference phase of the models for each file that is uploaded to the object storage used (e.g MinIO).
Read more