OSCAR is an open-source framework for data-processing serverless computing. Users upload files to an object storage which invokes a function responsible for processing each file. This runs on an elastic Kubernetes cluster, managed by the CLUES elasticity manager, that can be deployed on multiple Cloud providers thanks to the Infrastructure Manager (IM).
Functions can be chained to create data-driven serverless workflows which can run on different OSCAR clusters along several Cloud infrastructures. This way, the file-based output of a function is fed as input to another function through the corresponding object storage systems, thus using resources from multiple infrastructures.
OSCAR has been adapted to run on the edge by supporting the K3S minified distribution of Kubernetes. This way, it can run, for example, on ARM-based devices like clusters of Raspberry PIs such as the one depicted below:
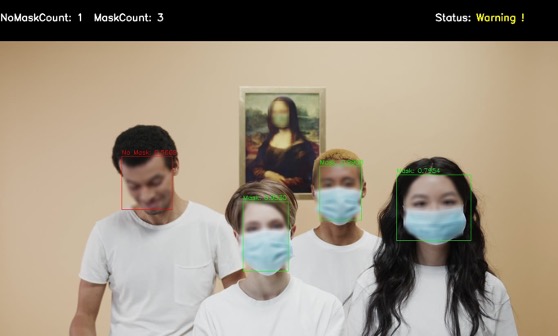
This allows to tackle a Deep Learning mask recognition use case to process anonymised images on the EGI Federated Cloud (a dynamically deployed OSCAR cluster) out of videos processed at the edge (the aforementioned cluster of Raspberry Pis). This allows to create a serverless workflows for event-driven processing along the Cloud-to-Edge Computing Continuum such as the one depicted below:
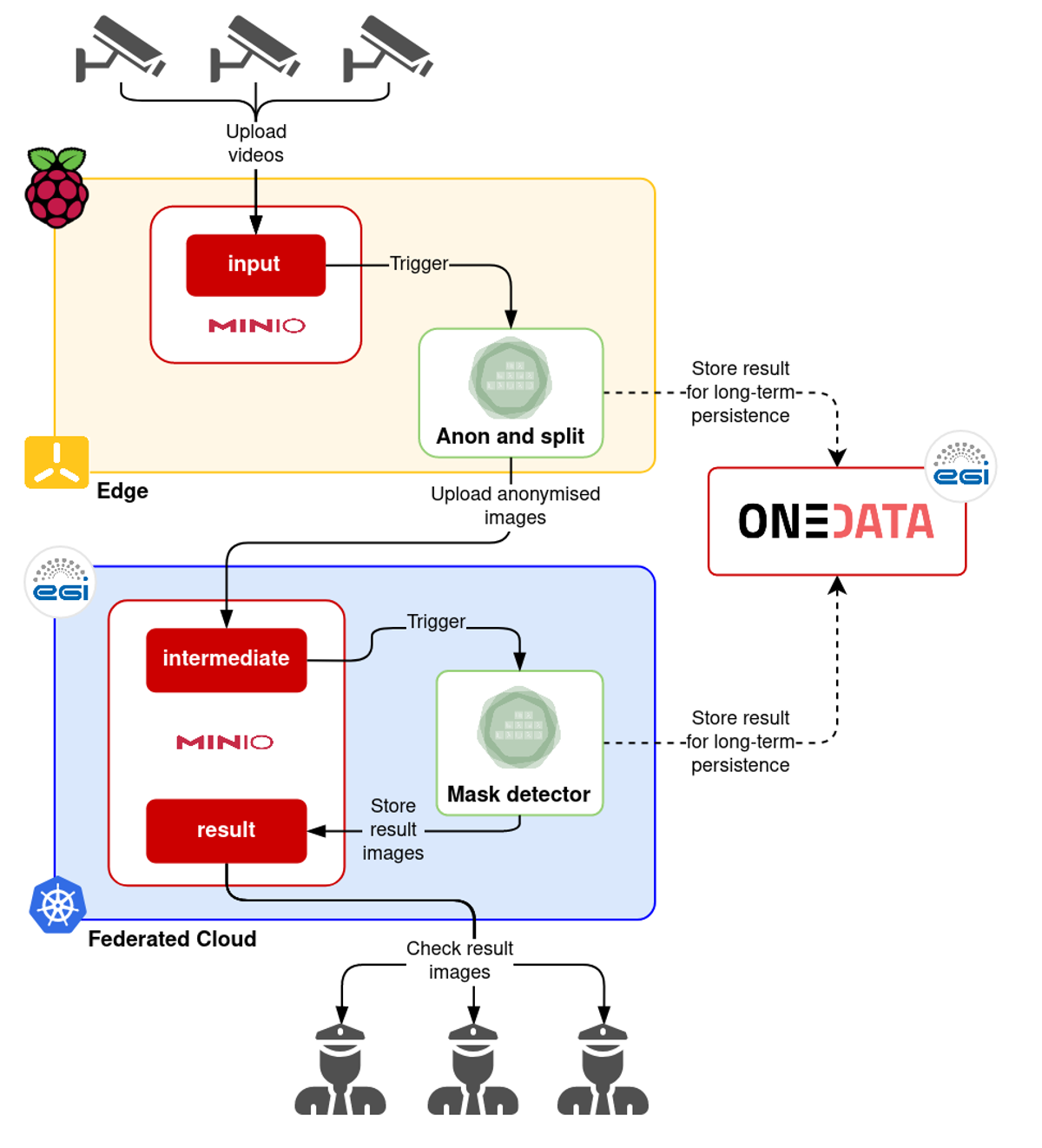
The videos are uploaded into the MinIO object storage in the OSCAR cluster running at the edge (in the Raspberry Pis), where they are split into sampled images that are later anonymised, applying a pre-trained Deep Learning model to blur the faces. These images are uploaded into the MinIO object storage in the OSCAR cluster running in the EGI Federated Cloud, where the mask detection procedure is applied. The resulting images are then further uploaded into the EGI DataHub (based on Onedata) for mid-term data storage.
This approach allows to perform data acquisition and anonymisation at the edge, as close as possible to where the data is being generated. This allows to implement Edge AI for inference, where AI algorithms are processed either directly on the device or as close as possible to the device generating the data. More computationally intensive tasks are delegated to IaaS Clouds, by using the very same software stack along the computing continuum, provided by OSCAR.
YouTube video
Here you have a video showing the platform action, as presented in the the EGI Conference 2021:
Here’s what you’ll see:
- Deploy an OSCAR cluster in the EGI Federated Cloud through the IM Dashboard
- Configure both clusters (Cloud and Edge) in OSCAR-CLI
- Show the Functions Definition Language (FDL) file to compose the workflow and the scripts of both services
- Deploy the workflow
- Perform a workflow execution:
- Upload a video to the MinIO input bucket in the OSCAR cluster at the edge.
- Show the logs in the OSCAR web interface
- Check that the result images are uploaded and compare them using BLISS
- Show the result files stored in the defined Onedata space
- Delete the deployed cluster.
OSCAR, IM, EC3, and CLUES are developed by the GRyCAP research group at the Universitat Politècnica de València.