What is OSCAR?
OSCAR is an open-source serverless platform for event-driven data-processing containerized applications that execute on elastic Kubernetes clusters that are dynamically provisioned on multiple Clouds.
OSCAR can be used as an effective serverless platform for scalable AI/ML model inference to achieve the following benefits:
- Ability to run AI model inference on disparate computing platform architectures, multiple Cloud providers and across the edge-to-cloud continuum, including your computer for easier testing.
- Seamless scalability for AI model inference regardless of the number of requests from your users, provided that the underlying computing platform provides enough hardware resources.
Here are the main reasons why.
#1: Elastic execution of Docker-based AI models

Docker is the most common approach to encapsulate applications, together with their dependencies, to guarantee successful execution across multiple computing platforms.
OSCAR runs containers for Docker-based AI applications in elastic Kubernetes clusters that grow and shrink, in terms of the number of nodes to adapt to the workload, within the elasticity boundaries defined by the user at deployment time
There is no need to adapt your AI application to run it as an OSCAR service. If your application runs as a command-line application, it will run within an OSCAR cluster. See some AI applications that are being used with OSCAR in the examples folder.
#2: Several AI inference execution approaches

Depending on the AI/ML model, inference might involve a computationally-intensive approach that requires GPU-based acceleration or it may require a quick response from the computational platform to provide fast feedback for the user.
Therefore, an OSCAR service can be invoked for AI/ML model inference using two approaches:
-
Synchronously: By leveraging the highly-elastic capabilities of KNative, the responses of the AI/model inference can be obtained with latency on the order of a second. Users can decide to keep alive a certain number of Pods to minimize the cold start.
-
Asynchronously. Data files on which to perform the model inference (e.g. images) are uploaded to the MinIO object-storage system deployed in the OSCAR cluster to trigger the execution of the OSCAR service as many times as files are to be processed. The elasticity of the cluster is managed by the CLUES elasticity system.
#3: Multiple user interfaces for AI model deployment
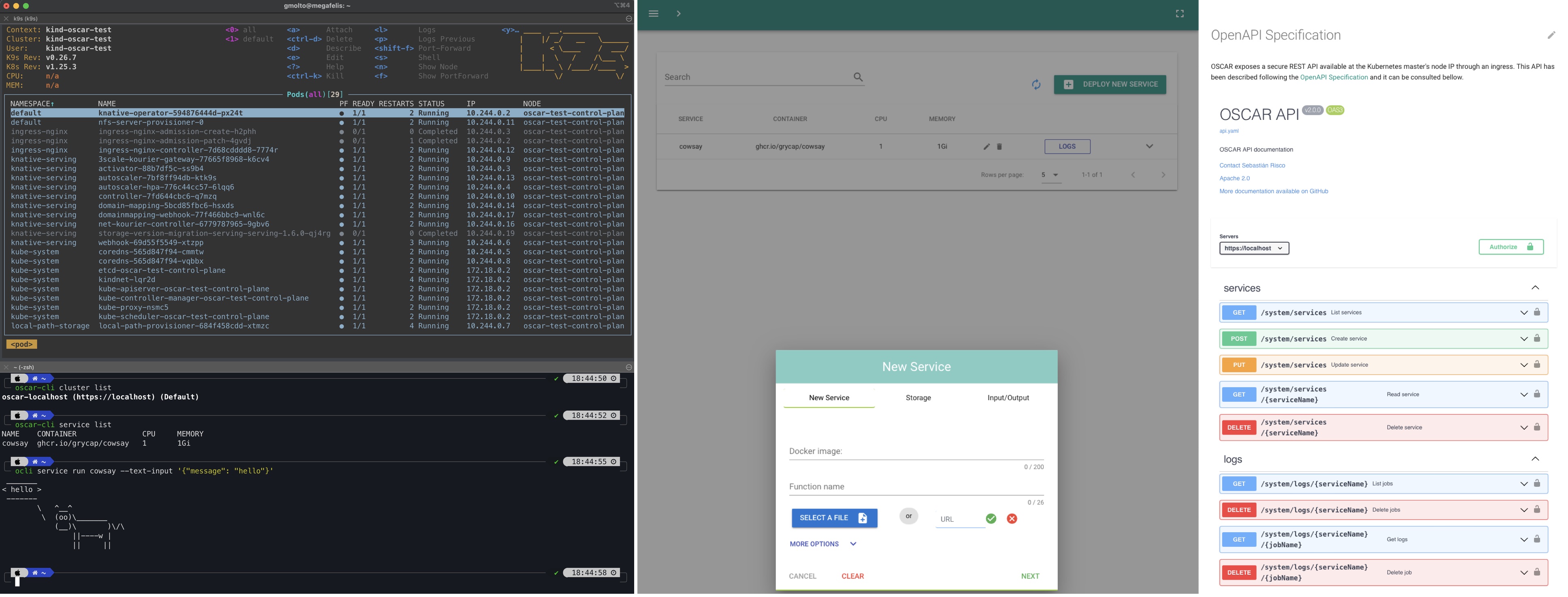
An AI practitioner may require different strategies to expose the AI model to be used for inference, such as programmatic, web-based interfaces, command-line, etc.
OSCAR provides the following approaches to deploy an AI model for inference:
-
OSCAR UI, is an easy-to-use web-based graphical user interface to log in with the dynamically generated credentials, or the ones you chose, at deployment time. It also supports OIDC and it is seamlessly integrated with EGI Check-In so that you can seamlessly log in with the credentials that you like.
-
OSCAR CLI, is a command-line interface that interacts with OSCAR clusters to manage the entire lifecycle of OSCAR services. These are defined in YAML-based documents using the Functions Definition Language (FDL).
-
REST API, is an Application Programming Interface (API) based on the OpenAPI specification that allows full programmatic access to the entire lifecycle management of OSCAR services.
-
Python API, a Python-based library to facilitate the interaction with OSCAR services through this programming language.
This way, you can easily integrate programmatic support via the REST API for the deployment of AI models within your CI/CD pipelines whenever the models are updated, while providing a fully-featured user experience through the CLI for advanced AI practitioners and a simple web-based UI for less savvy users.
#4: Integrates with existing AI model repositories

OSCAR executes Docker-based AI models from existing repositories such as the DEEP Open Catalog, the marketplace from the DEEP Hybrid DataCloud project, which delivers a comprehensive platform to easily develop, build, share and deploy Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning modules on top of distributed e-Infrastructures.
This work is being continued in the AI4EOSC project that will deliver an enhanced set services for the development of AI, ML and DL models and applications in the EOSC. The services will make use of advanced features such as distributed, federated and split learning; provenance metadata; event-driven data processing services or provisioning of AI/ML/DL services based on serverless computing.
#5: Runs on multiple platforms

OSCAR runs on Kubernetes clusters that can be dynamically deployed using the Infrastructure Manager (IM), an Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) tool that allows deploying complex virtual infrastructures across any Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Cloud that you have access to (e.g. Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, OpenStack, Open Telekom Cloud, etc.).
OSCAR can also be deployed on existing Kubernetes clusters using Helm and even in your local machine for testing on a sandboxed Kubernetes cluster using Kind that is dynamically deployed via a simple command (Docker is the only requirement):
curl -sSL http://go.oscar.grycap.net | bash
It supports amd64 and arm64 architectures, so it will run smoothly on a Mac with Apple Silicon.
OSCAR can also run on clusters of Raspberry Pis via the k3s lightweight Kubernetes distribution. This allows performing AI model inference at the edge of the network, as exemplified in the work on “serverless cloud-to-edge computing continuum approach for edge AI inference”.
#6. Runs along the computing continuum
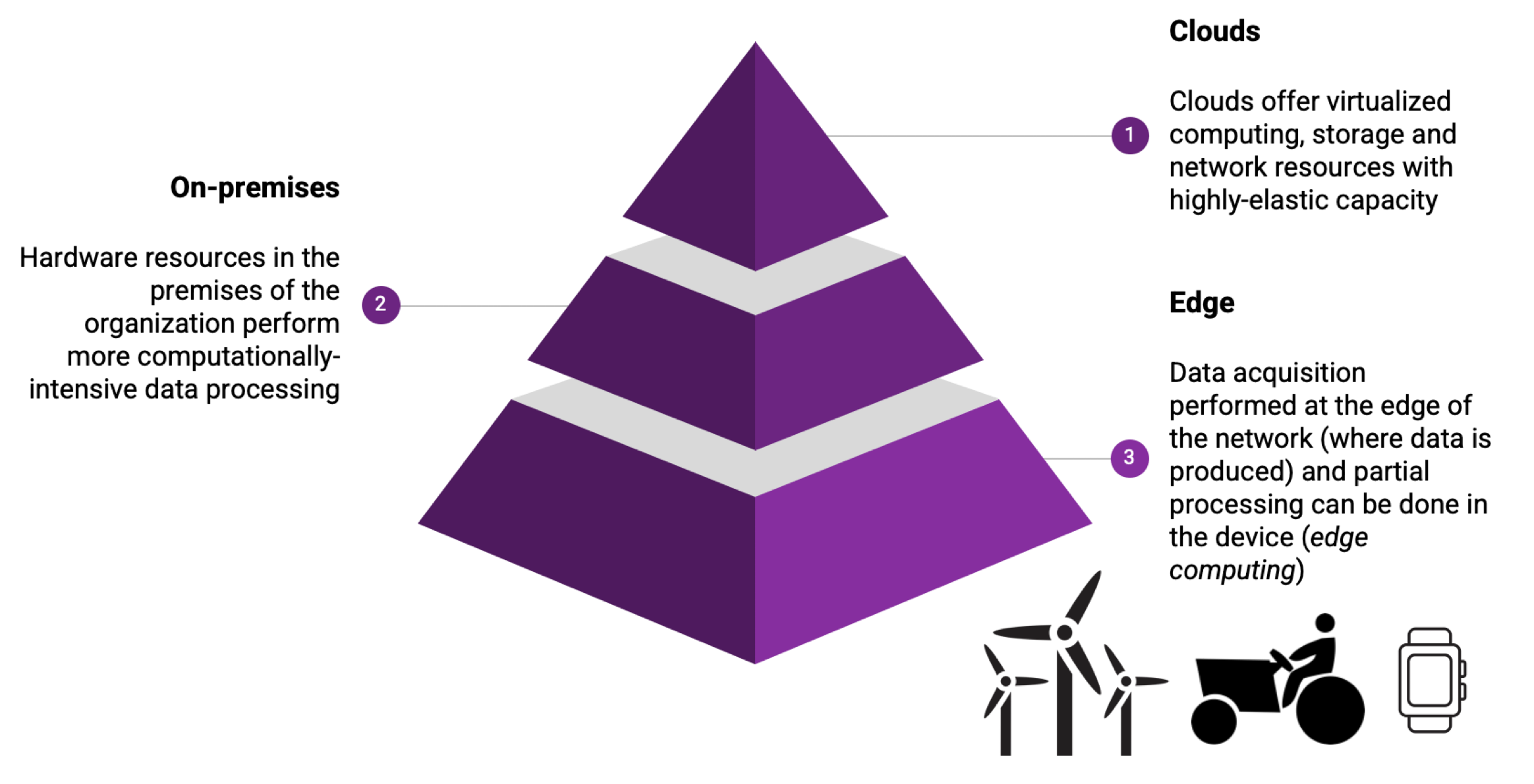
OSCAR supports a common Functions Definition Language (FDL) with SCAR, an open-source tool to create highly-parallel event-driven file-processing serverless applications that execute on customized runtime environments provided by Docker containers run on AWS Lambda and AWS Batch. This allows performing certain processing at the edge of the network close to where data is produced (e.g. on an OSCAR cluster deployed on top of a cluster of Raspberry Pis), e.g. for privacy-preserving reasons. Then carry out additional processing on an on-premises Cloud (e.g. on an OSCAR cluster deployed on an OpenStack-based cloud) and, finally, perform some compute-intensive bursty execution of jobs on AWS Lambda using SCAR.
This is exemplified in the work “event-driven inference of AI models for mask detection with the OSCAR serverless platform”.
#7: Supports data-driven workflow processing
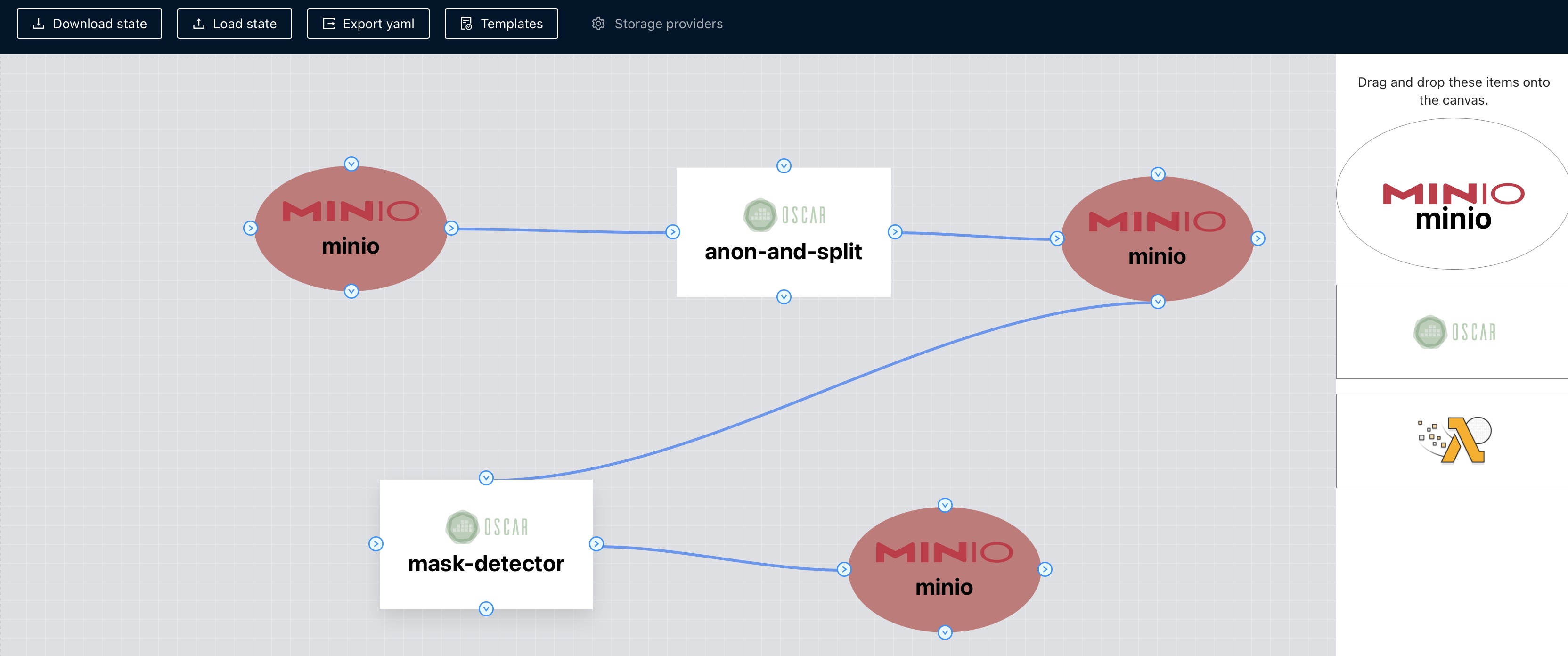
OSCAR services are typically linked to a MinIO object-storage bucket that triggers invocations whenever files are uploaded to perform the data processing. By chaining multiple OSCAR services, data-driven workflows along the computing continuum can be achieved.
The FDL Composer is an open-source tool, also accessible as a web-based application, to facilitate the definition of these workflows and automatically produce the corresponding FDL files. It supports different templates (e.g. two OSCAR services and three MinIO buckets) to avoid starting the definition of the workflow from scratch.
#8: Integrates with popular tools in the AI computing space

OSCAR integrates with the following tools:
- Docker, to use multi-arch container images for AI applications.
- Jupyter, to perform AI model inference from Jupyter notebooks via synchronous invocations to OSCAR services through the OSCAR’s Python API.
- EGI DataHub, implemented through Onedata, to provide long-term federated storage for the output of the AI model inference process.
- dCache, a system for storing and retrieving huge amounts of data, distributed among a large number of heterogenous server nodes, under a single virtual filesystem tree with a variety of standard access methods.
#9: Aligned with the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC)

The European Open Science Cloud (EOSC) is an environment for hosting and processing research data to support EU science.
In this regard, OSCAR complies with the Software Quality Assurance (SQA) baseline criteria for research projects identified in the EOSC-Synergy, having reached the silver badge assessed through the SQAaaS platform.
OSCAR uses the Infrastructure Manager (IM) to deploy the Kubernetes clusters on multiple Clouds. The IM is integrated in the EOSC Portal and it is being used in production (TRL 8) in the EGI Cloud Compute service.
#10: Completely open-source

OSCAR is developed entirely as an open-source component under the Apache 2.0 license through a group of active contributors.
OSCAR is being by the GRyCAP research group at the Universitat Politècnica de València.