In this post, we will learn about composing AI inference workflows by invoking OSCAR services with Elyra. This tool is an extension for Jupyter Notebooks and facilitates the graphical composition of pipelines, which allows us to easily compose a pipeline involving different OSCAR services. For that, we have recovered the next video demo that we invite you to watch. These developments are part of AI4-Compose, a component of the AI4OS stack, created in the AI4EOSC project.
About Elyra and EGI Notebooks
![]()
Let’s start by knowing a bit more about Elyra and EGI Notebooks, the service used in the video demo that provides users with a Jupyter Notebooks environment.
Elyra is an open-source extension for Jupyter Notebooks, designed to enhance the workflow of AI projects by supporting machine learning pipelines visually. It integrates seamlessly with various systems for orchestrating workflows, allowing users to create, run, and monitor their workflows within Jupyter environments. This tool is available inside EGI Notebooks, a service provided by the EGI cloud services that offer a cloud-based environment for running Jupyter Notebooks. This service simplifies the deployment and scaling of computational notebooks, providing researchers with powerful computational resources and a collaborative space for their scientific inquiries.
Invoking OSCAR services through Elyra allows users to graphically compose AI model inference pipelines. Let’s learn more about how Elyra works.
How does a workflow in Elyra work?
In Elyra, a workflow is a set of nodes or steps, each representing a script or notebook, connected in a flow that defines the execution order. Users can drag and drop nodes to create a visual representation of their workflow. Each node can be configured with specific parameters, inputs, and outputs. When a pipeline is run, Elyra executes the nodes sequentially or in parallel, depending on their dependencies. This visual approach not only simplifies the understanding and editing of machine learning workflows but also integrates with platforms like Kubeflow Pipelines and Apache Airflow to manage the execution in scalable environments.
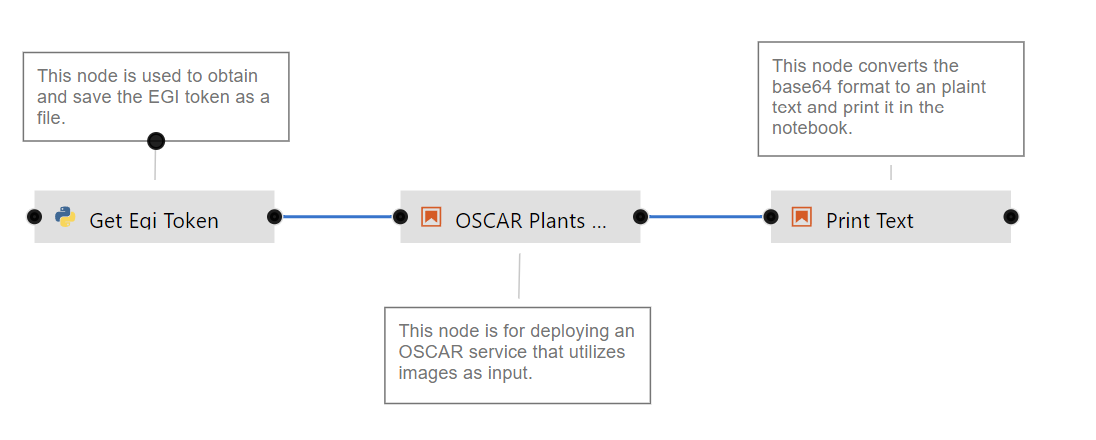
In the context of the AI4EOSC project, we have developed a set of recipes and nodes to simplify the execution of the AI model on its inference phase, that is previously created as a service on a remote OSCAR cluster. The examples that you see in the images above (“OSCAR Plants” and “OSCAR Gravify” boxes) and in the video demo can be found in the AI4Compose repository. Some of the nodes correspond with a model available for inference in the AI4EOSC Marketplace, like, for example, the Plants Species Classifier.
The easiest way to start testing the Elyra environment is to log in to EGI Notebooks and clone our AI4Compose repo with the examples and nodes, as shown in the video. Once done, you can start creating your own pipeline and add nodes that directly interact with an OSCAR cluster to invoke an already-defined OSCAR Service.
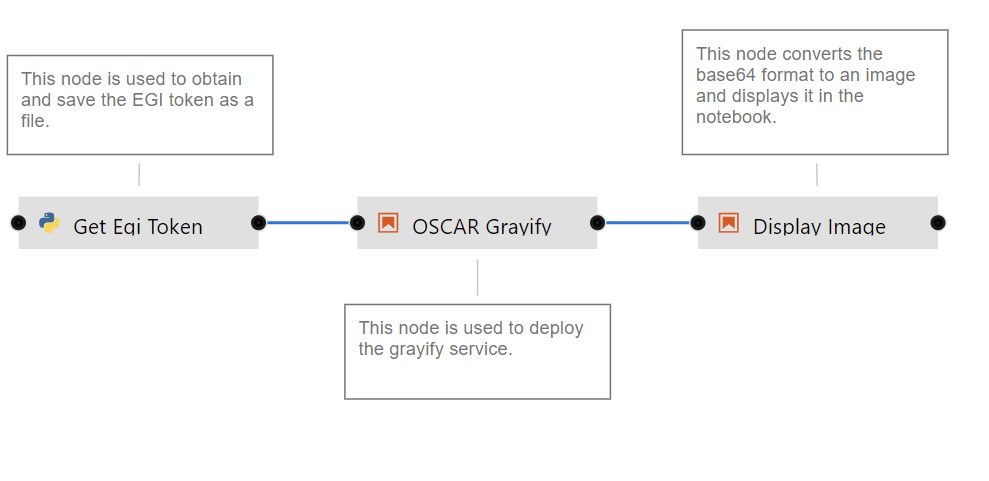
In the video, you can see that we have composed two different pipelines:
- Cowsay: this is the first toy example, where we use a custom module that interacts with the Cowsay OSCAR service that takes text as input and returns an ASCII art of a cow repeating the same text as output. This example is available here.
- Plant Classification workflow with input preprocessing: this second example shows how to compose a workflow for AI inference where two different OSCAR services are involved: the first one will convert the colour image of a plant to black and white and then, the second one classifies the plant to determine its species. The example is available here.
Deploying the pipeline
Once the pipeline has been created and all the nodes are properly connected, we can deploy it. Deploying a pipeline in Elyra involves three steps:
- Configuring the Nodes: Set up each node with the necessary parameters, such as file paths, environment variables, credentials, and dependencies. Watch the video for more details.
- Running the Pipeline: Execute the pipeline directly from Elyra, which will orchestrate the workflow based on the configured platform, such as local, Kubeflow, or Airflow.
- Monitoring Execution: Elyra provides tools to monitor the pipeline’s progress and debug if needed, ensuring that any issues can be addressed promptly. Watch the video demo to discover the ouptuts of the two example workflows.
This process enables users to efficiently manage complex workflows and automate the execution of OSCAR services, with the ability to interconnect them in a pipeline.
Summary
Elyra simplifies the execution of OSCAR services within the EGI Notebooks environment (and in general, in a Jupyter Notebooks environment), offering a user-friendly approach to managing complex pipelines. This post outlines how Elyra enhances productivity by streamlining processes, from repository cloning to workflow execution. For more information, there is a documentation entry in the official AI4OS docs repo, where you can find more details to start testing it.
We hope this overview inspires you to explore how to use OSCAR through Elyra in a Jupyter Notebooks environment (like the one provided by EGI Notebooks), helping you to leverage these powerful tools for your projects. Enjoy the innovative computing possibilities!